The round‐cut diamond is the most popular shape, accounting for 75% of all diamonds sold in most size. This shape’s popularity is attributed to the way it is cut, which, moreso than other shapes, allows it to beautifully reflect light.
For 8 carat diamond rings, round isn’t quite as popular a shape, as many people tend to choose elongated shapes like the oval or emerald cut. However, if you are looking for the the stone that sparkles the most, then an 8 carat round brilliant diamond would be the one to choose!
Rounds typically cost 25%‐35% more than fancy shapes because demand is high and yield is low. When compared to other shapes, more of the rough stone is lost in the cutting of a round diamond, raising the cost of each carat retained.
Most round diamonds are “brilliant‐cut”, containing 57 facets, or 58 if there is a culet.
Marcel Tolkowsky’s 1919 publication: “Diamond Design: A Study of the Reflection and Refraction of Light in Diamond,” described the ideal proportions of a round cut in order to maximize light return and dispersion.
The original Tolkowsky specifications are as follows: 53% table, 59.3% depth, 34.50 crown angle, visible culet. Due to theoretical and technological advancements, these parameters have since been perfected.SHOP ROUND DIAMONDS
CUT
The table below serves as a general guideline for evaluating the cut of a round diamond. GIA takes these and other factors into consideration when assigning a cut grade.
IDEAL | EXCELLENT | VERY GOOD | GOOD | FAIR | POOR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TABLE % | 53 – 58 | 52 – 53 or 58 – 60 | 51 or 61 – 64 | 50 or 65 – 69 | < 50 or > 69 | |
| DEPTH % | 58 – 62.3 | 59 – 62.3 | 58 – 58.9 or 62.4 – 63.5 | 57.5 – 57.9 or 63.6 – 64.1 | 56.5 – 57.4 or 64.2 – 65 | < 56.5 or > 65 |
| CROWN ANGLE | 34 – 34.7 | 34 – 34.9 | 32.1 – 33.9 or 35 – 35.9 | 30.1 – 32 or 36 – 37.9 | 29 – 30 or 38 – 40.5 | < 29 or > 40.5 |
| PAVILION DEPTH | 42.8 – 43.2 | 42 – 42.7 or 43.3 – 43.9 | 41 – 41.9 or 44 – 45.5 | 39 – 40.9 or 45.6 – 48 | < 39 or > 48 | |
| GIRDLE | Thin (1%) to Medium (3%) | Thin to Slightly Thin | Very Thin to Slightly Thick | Very Thin to Thick | Very Thin to Very Thick | Extra Thin to Extra Thick |
| CULET | None | Very Small | Small | Medium | > Medium | |
| L/W RATIO | 1.00 | 1.00 – 1.01 | 1.02 | > 1.02 |
When you’re looking for an 8 carat diamond, we recommend that you still prioritise cut quality, to ensure that your diamond sparkles brilliantly.
While a big diamond is impressive on its own, a big diamond that sparkles well is significantly more impressive!
COLOR
Color is another factor of diamond evaluation that is based purely on personal preference. Diamond colors range from D‐Z, with D being colorless and Z indicating a light yellow hue.
Many of these color distinctions are subtle and unrecognizable to the untrained eye, but these variations heavily impact price. Despite the appeal of diamonds in the D‐F range, many consumers are actually purchasing diamonds in the G‐I range because of the slight warmth they convey.
Below you’ll find a general guide for evaluating color in round diamonds.
EXCELLENT | VERY GOOD | GOOD | FAIR | POOR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < .50 CT | D – G | H – I | J – K | L – M | > M |
| .51 – 1.0 CT | D – G | H – I | J – K | L – M | > M |
| 1.0 – 2.0 CT | D – F | G – H | I – J | K – L | > L |
| > 2.0 CT | D – F | G | H | I – J | > J |
| FLUORO | NONE | FAINT – MED | STRONG | VERY STRONG |
CLARITY
Finally we come to clarity; another subjective matter, because every consumer has a specific standard.
When it comes to inclusions, some folks don’t mind it, while others will only take stones that appear eye‐clean and yet others still only wish to buy a flawless stone.
Check out this guide for clarity in round stones:
EXCELLENT | VERY GOOD | GOOD | FAIR | POOR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < .50 CT | FL – VS2 | SI1 – SI2 | I1 | I2 | > I2 |
| .51 – 1.0 CT | FL – VS1 | VS2 – SI1 | SI2 | I1 – I2 | > I2 |
| 1.0 – 2.0 CT | FL – VVS2 | VS1 – VS2 | SI1 – SI2 | I1 | > I1 |
| > 2.0 CT | FL – VVS2 | VS1 – VS2 | SI1 | SI2 | > SI2 |
All of these are of course just starting points, so if you’re looking at an 8 carat round diamond, you’ll need to inspect the individual diamond and ensure that you are comfortable with its level of clarity to ensure that no inclusions or flaws are visible to the naked eye.
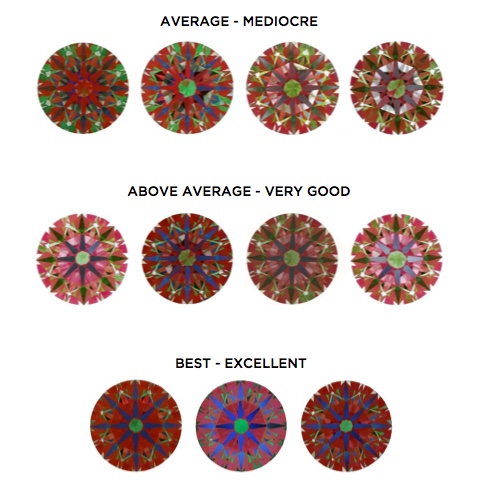
ASET & IDEALSCOPE
Both ASET and Idealscope images can help you to better exaluate the light performance of your diamond. Both tools will reveal areas of light leakage in white, but an ASET reading contains more detailed information. Because of this, it is the preferred method for evaluating fancy cut diamonds. However, because of the idealscope’s simplicity, it is a more user-friendly tool for non-gemologists. All you need to know when reading an idealscope is that white areas represent light leakage (bad) and red areas indicate light return (good).
Check out these images below for examples of ASET and Idealscope readings for round diamonds.


Hi, this is a comment.
To get started with moderating, editing, and deleting comments, please visit the Comments screen in the dashboard.
Commenter avatars come from Gravatar.